| 别称
IFN-G; IFG; IFI; INFr; IFN, Immune Interferon
| IFN-γ 简介
干扰素(IFN-γ,又称II型干扰素或免疫干扰素)是一种主要由T淋巴细胞和自然杀伤细胞产生的细胞因子。该蛋白与IFN-β或各种IFN-α家族蛋白没有明显的同源性。成熟的IFN-γ以非共价连接的同质体存在。IFN-γ最初是基于其抗病毒活性而被定性的。该蛋白还发挥抗增殖、免疫调节和促进炎症的活性,因此在宿主防御机制中很重要。IFN-γ诱导细胞因子的产生,上调I类和II类MHC抗原、Fc受体和白细胞粘附分子的表达。它调节巨噬细胞的效应功能,影响异型转换并增强B细胞分泌免疫球蛋白的能力。IFN-γ还能增强TH1细胞的扩增,并可能是TH1细胞分化所必需的。
| 特异性
可检测样本中小鼠的IFN-γ,且与其类似物无明显交叉反应。
| 典型数据及参考曲线
由于实验操作条件的不同( 如操作者、移液技术、洗板技术和稳定条件等),标准曲线的OD值会有所差异。以下数据和曲线仅供参考,实验者需根据自己的实验建立标准曲线。
| 浓度(pg/mL) |
200 |
100 |
50 |
25 |
12.5 |
6.25 |
3.12 |
0 |
| OD值 |
2.15 |
1.7 |
1.2 |
0.77 |
0.43 |
0.23 |
0.14 |
0.04 |
| 校正OD值 |
2.11 |
1.66 |
1.16 |
0.73 |
0.39 |
0.19 |
0.1 |
- |
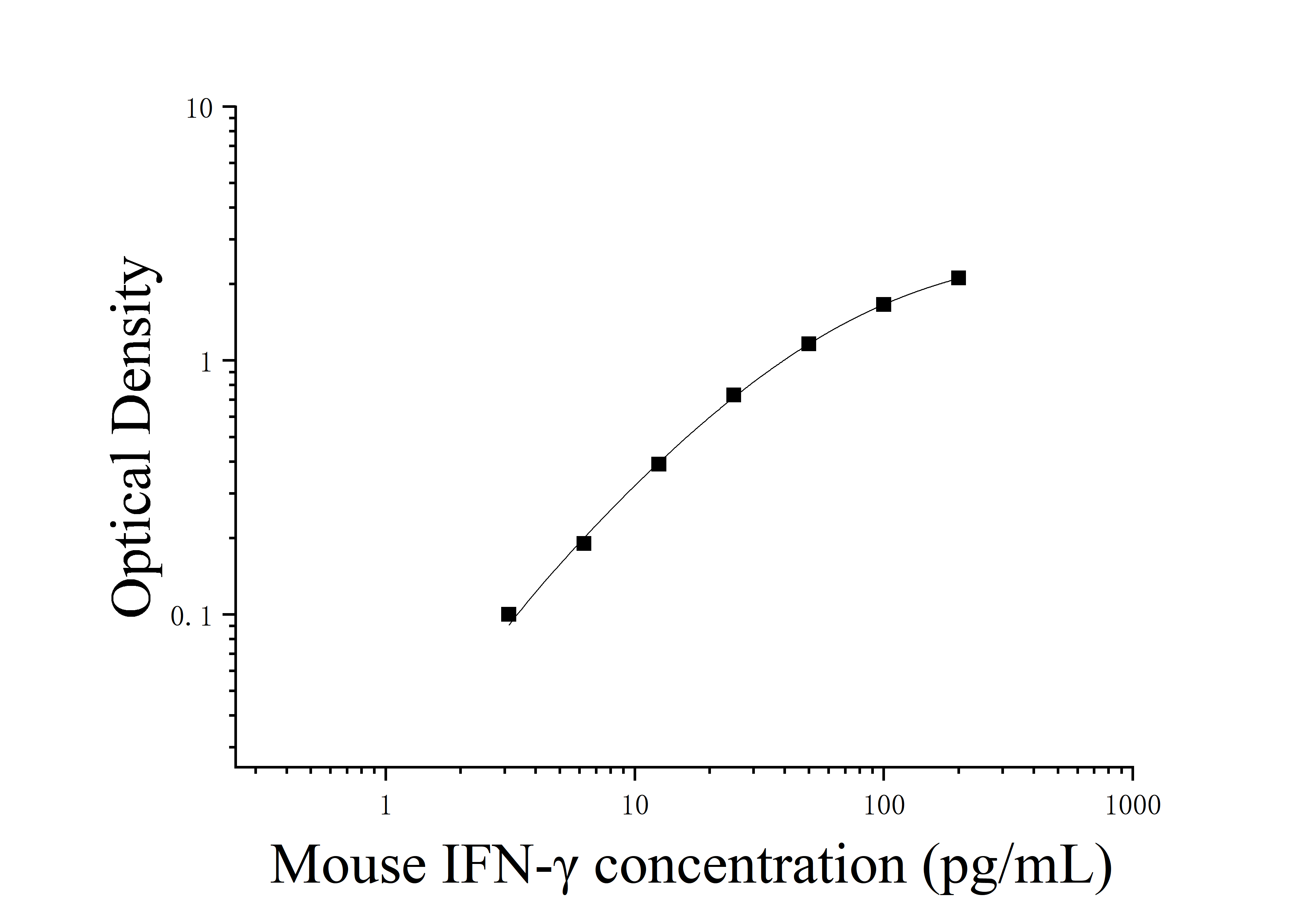
注意:本图仅供参考,应以同次试验标准品所绘标准曲线计算标本含量。
| 重复性
板内变异系数小于10%,板间变异系数小于10%
| 回收率
在选取的健康小鼠血清、血浆、细胞培养上清中加入3个不同浓度水平的小鼠IFN-γ,计算回收率
| 样本类型 |
范围 |
平均回收率 |
| 血清(n=8) |
84-101 |
96 |
| 血浆(n=8) |
92-108 |
103 |
| 细胞培养上清(n=8) |
96-110 |
106 |
| 线性稀释
分别在选取的4份健康小鼠血清、血浆、细胞培养上清中加入高浓度小鼠IFN-γ,在标准曲线动力学范围内进行稀释,评估线性。
| 稀释比例 |
回收率(%) |
血清 |
血浆 |
细胞培养上清 |
| 1:2 |
范围(%) |
84-95 |
88-100 |
90-110 |
| 平均回收率(%) |
91 |
93 |
98 |
| 1:4 |
范围(%) |
89-103 |
87-109 |
105-115 |
| 平均回收率(%) |
94 |
98 |
108 |
注:ELISA试剂盒检测范围等数据,因检测样本 的不同而调整,实际数据以随货说明书为准。
| ELISA操作视频


| ELISA操作前必读 / 下载








